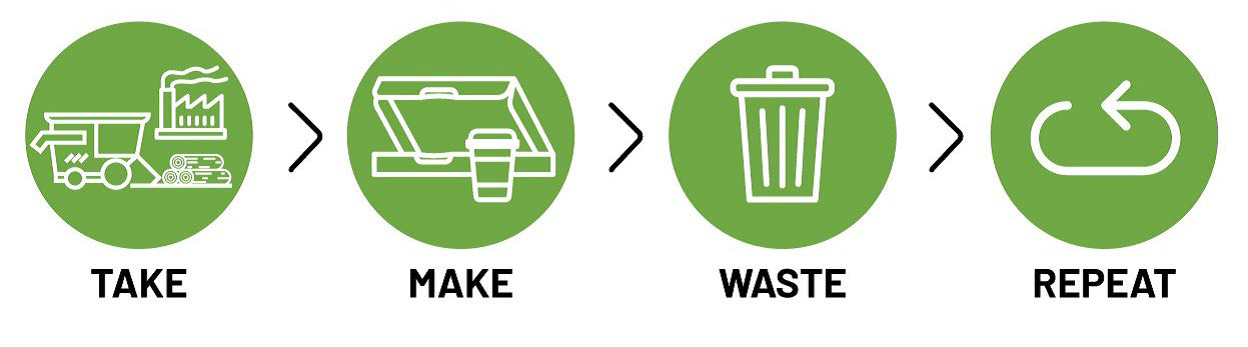
Electronic waste, or e-waste, is a term for electronic products that have become unwanted, non-working or obsolete, and have essentially reached the end of their useful life. As per E-waste Rule 2016, the E waste is defined as electrical and electronic equipment, whole or in part discarded as waste by the consumer or bulk consumer as well as rejects from manufacturing, refurbishment, and repair processes. E-waste contains many valuable, recoverable materials such as aluminium, copper, gold, silver, plastics, and ferrous metals. In order to conserve natural resources and the energy needed to produce new electronic equipment from virgin resources, electronic equipment can be refurbished, reused, and recycled instead of being landfilled.
Under the guidelines of the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India, E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2016 and M/S. A&T Video Networks Private Limited (A&T) stands committed to implement E-Waste Rules.
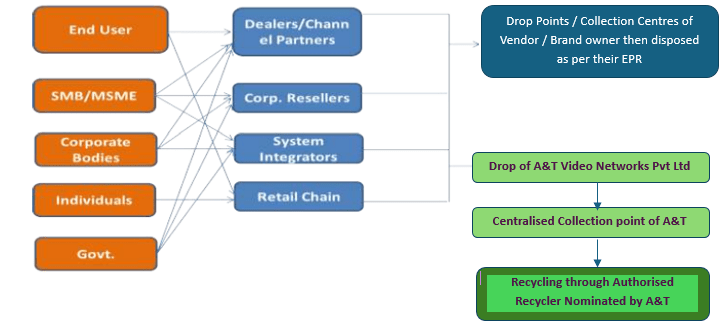
A&T understand there is a need to encourage recycling of all useful and valuable material from e-waste so as to conserve the ever-depleting natural resources. Recycling end-of-life discarded products is vital if we are to save resources and minimize landfill A&T understands its responsibility and in this regards we have tied-up with one of the leading PRO namely TES-AMM (INDIA) PVT. LTD. for facilitating our customers to enable them to dispose of e-waste products after its end-of-life. Authorized EPR ID: 826 _ Dated: 9th September, 2023.